| Grumman | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
S-2 / S2F Tracker
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Photo: Robert Deering Location 1 Location 2 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
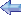
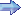
The Grumman S-2 (S2F) "Tracker" was developed and first flown in 1952 to replace hunter/killer aircraft for anti-submarine warfare operations. Design criteria required that the aircraft accommodate air-to-underwater guided missile torpedoes and associated electronic equipment, and be capable of long-range search missions at low altitudes while flying in all-weather conditions from an aircraft carrier.
The "Tracker" could be equipped with up to 32 sono-buoys, an APS-38 search radar in a retractable radome, and magnetic anomaly detection (MAD) gear. Armament included a fuselage weapons-bay for one depth-bomb or two homing torpedoes and six underwing pylons capable of handling depth-bombs, torpedoes or rockets. The first of 755 production model S-2s entered service in 1954 and soon established themselves as the Navy's front line carrier based ASW air-craft. Later versions carried "Jezebel" passive long-range acoustic search equipment and "Julie" explosive echo-sounding equipment. Powered by two 1,525 hp Wright engines and manned by a crew of four (two pilots, two radar operators), the S-2 grossed out at 26,867 lbs, had a maximum speed of 253 mph and a range of 1150 statute miles. |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
VARIANTS:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||

%20Tracer%20-%20Grumman%20(Intrepid17)%20(8X4).jpg)
%20(8X3.6).jpg)