| Curtiss | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
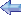
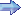
AT-9 Fledgling
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
%20(8X4).jpg) |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Photo:
Robert Deering 10/18/2012 National Museum of the USAF Wright-Patterson AFB (FFO) Dayton, Ohio |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| The AT-9 advanced trainer was used to bridge the gap between single-engine trainers and twin-engine combat aircraft. The prototype first flew in 1941, and the production version entered service in 1942. The prototype had a fabric-covered steel tube fuselage and fabric-covered wings, but production AT-9s were of stressed metal skin construction. The AT-9 was not easy to fly or land, making it particularly suitable for teaching new pilots to cope with the demanding flight characteristics of a new generation of high-performance, multi-engine aircraft such as the Martin B-26 and Lockheed P-38. Although the AT-9 originally bore the nickname "Fledgling," it was more widely known as the "Jeep." Four hundred ninety-one AT-9s and 300 AT-9As were built before production ended in February 1943. | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||