| Boeing | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
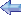
WB-50 Superfortress
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
%20(7.4X4).jpg) |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Photo:
Robert Deering 10/18/2012 National Museum of the USAF Wright-Patterson AFB (FFO) Dayton, Ohio |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
The B-50, the last
propeller-driven bomber delivered to the
U.S. Air Force, made its initial flight on
June 25, 1947. Basically an improved version
of the
B-29, this
aircraft's large number of modifications
caused its redesignation as the B-50.
Between 1948 and 1954, B-50s served with the
Strategic Air Command as medium bombers, and
they were replaced by jet-propelled
B-47s. Many
were modified for support roles such as
weather reconnaissance, crew training,
photo-mapping and aerial refueling.
In 1953 the USAF decided to replace its aging WB-29 weather reconnaissance aircraft with modified B-50Ds. Stripped of their defensive armament, 36 B-50Ds were equipped for long-range weather reconnaissance missions with high-altitude atmospheric samplers, Doppler radar, weather radar and a bomb-bay fuel tank for extended range. Some WB-50 aircraft also flew missions to sample the air for radioactive particles indicating that the Soviet Union had detonated a nuclear weapon. The WB-50D aircraft accomplished special weather reconnaissance missions with SAC's 97th Bomb Wing until April 1955, when all WB-50s went to the Air Weather Service. In 1963 the USAF started phasing out the WB-50Ds, and in 1965 the aircraft on display became the last WB-50D to be retired. It was delivered to the museum in 1968. |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
VARIANTS:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||

%20(8X4).jpg)