| Boeing | ||||
|
H-47 Chinook
|
||||
%20(8X4).jpg) |
||||
|
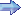
Photo: Robert Deering 1969 Idlewild AAF (A805) Taegu, Korea |
||||
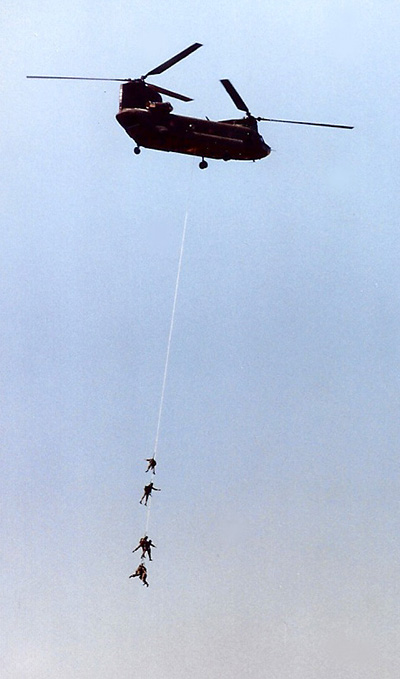
| The Boeing CH-47 Chinook is an American twin-engine, tandem rotor heavy-lift helicopter. Its primary roles are troop movement, artillery emplacement and battlefield resupply. It has a wide loading ramp at the rear of the fuselage and three external-cargo hooks. With a top speed of 170 knots (196 mph, 315 km/h) the helicopter is faster than contemporary utility and attack helicopters of the 1960s. The CH-47 is among the heaviest lifting Western helicopters. Its name is from the Native American Chinook people.The Chinook was designed and initially produced by Boeing Vertol in the early 1960s; it is now produced by Boeing Rotorcraft Systems. It is one of the few aircraft of that era – along with the fixed-wing Lockheed C-130 Hercules cargo aircraft – that remain in production and front-line service, with over 1,179 built to date. The helicopter has been sold to 16 nations with the U.S. Army and the Royal Air Force (see Boeing Chinook (UK variants)) its largest users. | ||||
|
Design and Development Early developmentIn late 1956, the United States Department of the Army announced plans to replace the Sikorsky CH-37 Mojave, which was powered by piston engines, with a new, turbine-powered helicopter. Turbine engines were also a key design feature of the smaller UH-1 "Huey" utility helicopter. Following a design competition, in September 1958, a joint Army–Air Force source selection board recommended that the Army procure the Vertol medium transport helicopter. However, funding for full-scale development was not then available, and the Army vacillated on its design requirements. Some in the Army aviation corps thought that the new helicopter should be a light tactical transport aimed at taking over the missions of the old piston-engined H-21 and H-34 helicopters, and consequently capable of carrying about fifteen troops (one squad). Another faction in the Army aviation corps thought that the new helicopter should be much larger to be able to airlift a large artillery piece, and have enough internal space to carry the new MGM-31 "Pershing" Missile System. Vertol began work on a new tandem-rotor helicopter designated Vertol Model 107 or V-107 in 1957. In June 1958, the U.S. Army awarded a contract to Vertol for the aircraft under the YHC-1A designation. The YHC-1A had a capacity for 20 troops. Three were tested by the Army for deriving engineering and operational data. However, the YHC-1A was considered by most of the Army users to be too heavy for the assault role and too light for the transport role. The decision was made to procure a heavier transport helicopter and at the same time upgrade the UH-1 "Huey" as a tactical troop transport. The YHC-1A would be improved and adopted by the Marines as the CH-46 Sea Knight in 1962. The Army then ordered the larger Model 114 under the designation HC-1B. The pre-production Boeing Vertol YCH-1B made its initial hovering flight on 21 September 1961. In 1962 the HC-1B was redesignated the CH-47A under the 1962 United States Tri-Service aircraft designation system. It was named "Chinook", which alludes to the Chinook people of the Pacific Northwest.T The CH-47 is powered by two turboshaft engines, mounted on each side of the helicopter's rear pylon and connected to the rotors by driveshafts. Initial models were fitted with Lycoming T-53 jet engines with a combined rating of 2,200 shaft horsepower. Subsequent versions of the Chinook were configured with improved Lycoming engines and later with General Electric turbines. The counter-rotating rotors eliminate the need for an anti-torque vertical rotor, allowing all power to be used for lift and thrust. The ability to adjust lift in either rotor makes it less sensitive to changes in the center of gravity, important for the cargo lifting role. If one engine fails, the other can drive both rotors. The "sizing" of the Chinook was directly related to the growth of the Huey and the Army's tacticians' insistence that initial air assaults be built around the squad. The Army pushed for both the Huey and the Chinook, and this focus was responsible for the acceleration of its air mobility effort. Improved and Later Versions Improved and more powerful versions of the CH-47 have been developed since the helicopter entered service. The U.S. Army's first major design leap was the now-common CH-47D, which entered service in 1982. Improvements from the CH-47C included upgraded engines, composite rotor blades, a redesigned cockpit to reduce pilot workload, improved and redundant electrical systems, an advanced flight control system and improved avionics. The latest mainstream generation is the CH-47F, which features several major upgrades to reduce maintenance, digitized flight controls, and is powered by two 4,733-horsepower Honeywell engines. A commercial model of the Chinook, the Boeing-Vertol Model 234, is used worldwide for logging, construction, fighting forest fires, and supporting petroleum extraction operations. On 15 December 2006, the Columbia Helicopters company of the Salem, Oregon, metropolitan area, purchased the Type certificate of the Model 234 from Boeing. The Chinook has also been licensed to be built by companies outside of the United States, such as Elicotteri Meridionali (now AgustaWestland) in Italy, Kawasaki in Japan. Operational History Vietnam War The Army finally settled on the larger Chinook as its standard medium transport helicopter and as of February 1966, 161 aircraft had been delivered to the Army. The 1st Cavalry Division had brought their organic Chinook battalion with them when they arrived in 1965 and a separate aviation medium helicopter company, the 147th, had arrived in Vietnam on 29 November 1965. This latter company was initially placed in direct support of the 1st Infantry Division. The CH-47s are generally armed with a single 7.62-millimeter M60 machine gun on a pintle mount on either side of the machine for self-defense, with stops fitted to keep the gunners from firing into the rotor blades. Dust filters were also added to improve engine reliability. At its peak employment in Vietnam, there were 22 Chinook units in operation. Of the nearly 750 Chinook helicopters in the U.S. and South Vietnam fleets, about 200 were lost in combat or wartime operational accidents. The U.S. Army CH-47s supported the 1st Australian Task Force as required. |
||||
|

%20(1)%20(7.2X4).jpg)
%20(3)%20(8X4).jpg)
