| Sikorsky | ||||||||||||
|
H-19 /
HRS Chickasaw
|
||||||||||||
.jpg) |
||||||||||||
|
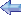
Photo: Robert Deering 1969 Idlewild AAF (A805) Taegu, Korea |
||||||||||||
| The Sikorsky H-19 Chickasaw, (also known by its Sikorsky model number, S-55) was a multi-purpose helicopter used by the United States Army and United States Air Force. It was also license-built by Westland Aircraft as the Westland Whirlwind in the United Kingdom. United States Navy and United States Coast Guard models were designated HO4S, while those of the U.S. Marine Corps were designated HRS. In 1962, the U.S. Navy, U.S. Coast Guard and U.S. Marine Corps versions were all redesignated as H-19s like their U.S. Army and U.S. Air Force counterparts | ||||||||||||
Design and developmentThe H-19's first flight was on 10 November 1949 and it entered operations in 1950. Over 1,000 of the helicopters were manufactured by Sikorsky for the United States. An additional 550 were manufactured by licensees of the helicopter including Westland Aircraft, the SNCASE in France and Mitsubishi in Japan. The helicopter was widely exported, used by many other nations, including Portugal, Greece, Israel, Chile, South Africa, Denmark and Turkey. In 1954 the Marines tested an idea to assist the rotors lift better in hot or high climates and if the helicopter was overloaded, by installing a rocket nozzle at the tip of each rotor blade with the fuel tank located in the center above the rotor blade hub. Enough fuel was provided for seven minutes of operation. The H-19 Chickasaw holds the distinction of being the US Army's first true transport helicopter and, as such, played an important role in the initial formulation of Army doctrine regarding air mobility and the battlefield employment of troop-carrying helicopters. The H-19 underwent live service tests in the hands of the 6th Transportation Company, during the Korean War beginning in 1951 as an unarmed transport helicopter. Undergoing tests such as medical evacuation, tactical control and front-line cargo support, the helicopter succeeded admirably in surpassing the capabilities of the H-5 Dragonfly which had been used throughout the war by the Army. The U.S. Air Force ordered 50 H-19A's for rescue duties in 1951. These aircraft were the primary rescue and medical evacuation helicopters for the USAF during the Korean War. The Air Force continued to use the H-19 through the 1960s, ultimately acquiring 270 of the H-19B model. France made aggressive use of helicopters in Algeria, both as troop transports and gunships, Piasecki/Vertol H-21 and Sud-built Sikorski H-34 helicopters rapidly displaced fixed-wing aircraft for the transport of paras and quick-reaction commando teams. In Indochina, a small number of Hiller H-23s and Sikorsky H-19s were available for casualty evacuation. In 1956, the French Air Force experimented with arming the H-19, then being superseded in service by the more capable Piasecki H-21 and Sikorsky H-34 helicopters. The H-19 was originally fitted with a 20-mm cannon, two rocket launchers, two 12.7-mm machine guns, and a 7.5-mm light machine gun firing from the cabin windows, but this load proved far too heavy, and even lightly armed H-19 gunships fitted with flexible machine guns for self-defense proved underpowered. The H-19 was also used in the early days of the Vietnam War before being supplanted by the Sikorsky H-34 Choctaw, which was based on the H-19. |
||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||

%20(6X4).jpg)