| Cessna | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
T-41 Mescalero
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
%20(8X4).jpg) |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
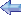
T-41A Photo: Robert Deering 10/18/2012 National Museum of the USAF Wright-Patterson AFB (FFO) Dayton, Ohio |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| The Cessna T-41 Mescalero is a military version of the popular Cessna 172, operated by the United States Air Force and Army, as well as the armed forces of various other countries as a pilot-training aircraft. | ||||||||||||||||||||||
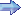
.jpg) T-41B Photo: Robert Deering 1968 Wright AAF (LHW) Fort Stewart, Georgia |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
DESIGN AND DEVELOPMENT In 1964, the US Air Force (USAF) decided to use the off-the-shelf Cessna 172F as a lead-in aircraft for student pilots rather than starting them out in the T-37 jet aircraft. The USAF ordered 237 T-41As from Cessna. The first USAF class (67-A) of students began training on the T-41 from the civilian airport in Big Spring, Texas, in August 1965. The T-41B was the US Army version, with a 210 hp (160 kW) Continental IO-360 engine and constant-speed propeller in place of the 145 hp (108 kW) Continental O-300 and 7654 fixed-pitch propeller used in the 172 and the T-41A. In 1968, the USAF acquired 52 of the more powerful T-41Cs, which used 210 hp (160 kW) Continental IO-360 and a fixed-pitch climb propeller, for use at the Air Force Academy in Colorado Springs. In 1996, the aircraft were further upgraded to the T-41D, which included an upgrade in avionics and to a constant-speed propeller. Beginning in 1993, the USAF replaced many of the T-41 fleet with the Slingsby T-3A Firefly for the flight-screening role, and for aerobatic training, which was outside the design capabilities of the T-41. The T-3A fleet was indefinitely grounded in 1997 and scrapped in 2006 following a series of fatal accidents at the US Air Force Academy. The USAF now trains all its prospective pilots and combat systems officers through a civilian contract with DOSS Aviation known as initial military flight screening, which makes use of the Diamond DA20. This program is conducted for USAF line officer accession programs (e.g., USAFA, AFROTC, and OTS), with said training taking place after these officers have been commissioned as second lieutenants. It is also conducted for USAF officers at the first lieutenant and captain level selected for flight training after an assignment as a non-aeronautically rated officer. Four T-41s remain at the Air Force Academy for the USAFA Flying Team, as well as to support certain academic classes. A number of air forces, including Saudi Arabia and Singapore, purchased various civilian models of the Cessna 172 for use in military training, transport, and liaison roles. While similar to the T-41, these aircraft were not T-41s and were powered by the standard 172 powerplants available in the model year purchased. These included the 145 hp (108 kW) Continental O-300 in pre-1968 aircraft and the 150 and 160 hp (120 kW) Lycoming O-320 in later 172s. |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||

%20(8X4).jpg)
%20(8X4).jpg)
.jpg)